4 Minutes
Comprehensive 24-Year Study Confirms Safety of Aluminum Salts in Childhood Vaccines
One of the most extensive epidemiological studies ever conducted on childhood vaccinations has delivered conclusive evidence supporting the safety of aluminum-based adjuvants—a common vaccine additive. Over 24 years, Danish researchers analyzed health data from more than 1.2 million children, providing robust reassurance for parents worldwide who are concerned about vaccine safety.
Scientific Context: Understanding Aluminum Adjuvants
Aluminum salts have been employed as adjuvants in non-live vaccines for over seven decades. Adjuvants are essential components that amplify the immune system’s response to a vaccine, enabling effective immunization with lower doses of antigen. Despite their long and well-documented track record, aluminum-containing adjuvants have repeatedly been cited in vaccine safety debates, with claims—often unsupported—linking them to chronic conditions such as autism, asthma, and various neurodevelopmental or autoimmune disorders.
Contrary to misconceptions, the chemical form of aluminum used in these adjuvants is distinctly different from the pure metal. Epidemiologist Dr. Anders Hviid, senior author of the study from the Statens Serum Institute in Denmark, emphasizes, “We are not injecting metal into children." He adds, “Our study addresses many of these concerns and provides clear and robust evidence for the safety of childhood vaccines.”
Massive Cohort Study: Methods and Main Findings
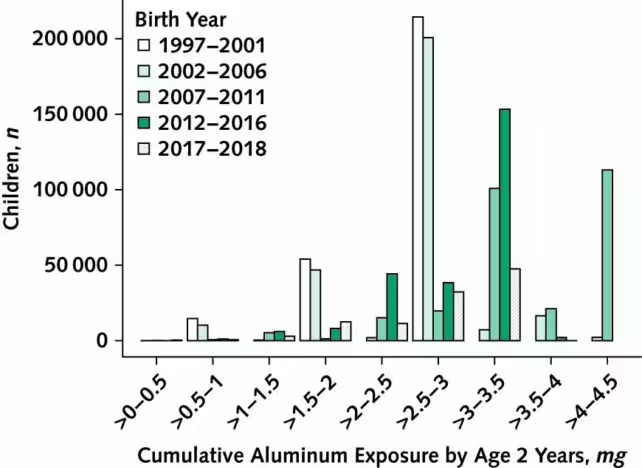
From 1997 to 2020, Dr. Hviid and his colleagues leveraged Denmark’s comprehensive nationwide health registry to track vaccinations, diagnoses, and potential confounding factors in children. This immense data set allowed researchers to compare children who were vaccinated during periods with lower versus higher recommendations for aluminum-containing vaccines. The analysis focused on possible links between early exposure to aluminum salts (before age two) and the subsequent development of 50 chronic disorders, including 36 autoimmune, 9 allergic, and 5 neurodevelopmental conditions.
The key result? There was no significant evidence that increased exposure to aluminum salts in childhood vaccines raises the risk for any of these chronic diseases. Furthermore, the study found no dose-dependent relationship—meaning higher exposure did not correlate with elevated health risks.
Independent experts have praised the project’s rigor. Dr. Edward Belongia, a veteran epidemiologist who has researched vaccine safety for decades, described it as “the largest and most definitive observational study on the safety of vaccine-related aluminum exposure in children.” He further noted that the findings should “put to rest any lingering doubts” regarding health risks related to aluminum in vaccines.
Debunking Myths: Context Around Aluminum Exposure
While some animal studies have raised potential neurotoxicity concerns at high aluminum doses, those scenarios differ dramatically from real-life childhood vaccinations. In fact, the aluminum exposure from vaccines is minimal when compared to other environmental and dietary sources present in daily life. For instance, the average adult’s diet provides around 7 to 9 milligrams of aluminum per day through plants, water, and processed foods.
According to research, the total aluminum received from all recommended vaccines in an infant’s first six months is approximately 4.4 milligrams. For comparison, breastfed infants ingest about 7 milligrams of aluminum in the same timeframe from breast milk, and formula-fed infants receive up to 38 milligrams from formula.
The body efficiently processes and eliminates aluminum introduced via vaccination. Studies tracking aluminum levels in infants’ blood and hair post-vaccination show no accumulation or rise in overall aluminum concentration. The World Health Organization (WHO) affirms that aluminum levels after vaccination consistently remain well below established safety thresholds, including for low birth-weight babies.
Global Health Implications and the Importance of Vaccination Science
Aluminum adjuvants play a crucial role in the effectiveness of routine childhood immunizations, significantly reducing the incidence of severe infectious diseases. Notably, global immunization efforts prevent an estimated four million deaths annually. The scientific consensus, reinforced by large-scale studies like this one, indicates not only the safety—but also the indispensability—of vaccines containing aluminum salts for protecting children’s health.
Conclusion
This landmark Danish study offers robust, large-scale evidence dispelling fears about aluminum-containing vaccine adjuvants. The absence of links between early-life aluminum exposure from vaccines and chronic health conditions underscores the vital safety and benefit profile of childhood immunizations. In the face of ongoing misinformation and skepticism, this research stands as a key pillar supporting public trust in vaccination science, affirming that childhood vaccines save millions of lives each year without posing additional long-term health risks.
Source: acpjournals


Comments