4 Minutes
Exploring the Link Between Ocean Proximity and Longevity
A growing body of research suggests that one's environment can significantly impact overall health and longevity. While factors such as diet, exercise, and social connections are well-established as contributors to a long life, recent scientific studies indicate that living near the ocean may also play a meaningful role in extending lifespan.
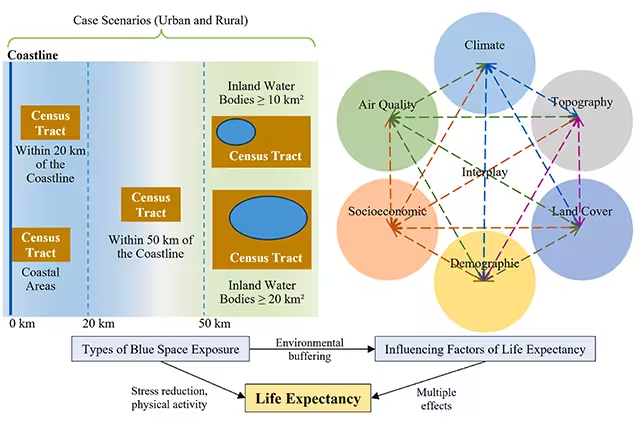
A comprehensive study conducted by researchers at Ohio State University examined census records from 66,263 individuals, aiming to understand how proximity to water—especially the coastline—correlates with overall lifespan. The project builds on the concept of "blue spaces," which refers to visible bodies of water such as oceans, lakes, and rivers. Previous research has shown that blue spaces contribute to mental health and well-being, but this new analysis delves deeper into their impact on physical longevity.
Key Findings: Coastal Living Versus Urban Inland Waters
The Ohio State University team found compelling evidence that people residing near the coast tend to live longer lives compared to those living in urban areas adjacent to rivers or lakes. Data analysis revealed that coastal residents exceeded the average life expectancy of 79 years by at least one year, whereas individuals living in urban inland communities had a slightly lower life expectancy, averaging around 78 years.
Environmental health scientist Jianyong Wu, one of the study's lead authors, explained, "Overall, the coastal residents were expected to live a year or more longer than the 79-year average, and those who lived in more urban areas near inland rivers and lakes were likely to die by about 78 or so."
This correlation, while strong, is not definitive proof of direct causation. Multiple environmental and socioeconomic influences likely contribute to these trends, warranting further investigation.
Potential Factors Behind the Coastal Advantage
The researchers identified several possible explanations for the positive relationship between ocean proximity and longevity. Coastal regions generally experience milder climates, with fewer temperature extremes and improved air quality compared to many urban environments. Access to recreational opportunities and outdoor activities also tends to be greater in these areas, which can foster healthier, more active lifestyles.
Socioeconomic factors may also play a pivotal role, as coastal properties are often more expensive, potentially attracting residents with increased access to quality healthcare and other resources that promote well-being.
Rural Versus Urban Inland Blue Spaces
The study further distinguished between rural and urban residents living near inland bodies of water. People in rural communities near lakes or rivers did enjoy a modest increase in life expectancy, but the benefit was less pronounced than that observed among coastal dwellers. In urban settings, however, any health benefits associated with blue spaces appeared to be negated by environmental challenges and lifestyle factors.
Ecological geographer Yanni Cao, a co-author, noted, "Pollution, poverty, lack of safe opportunities to be physically active, and an increased risk of flooding are likely drivers of these differences."
Implications and Future Research
This research highlights the complex interplay between natural environments and human health. While the advantages of living near blue spaces are well-documented, urbanization seems to diminish or even reverse some of those benefits. The findings support the broader hypothesis that nature plays a vital role in promoting health, but also emphasize how socioeconomic disparities and urban environmental stressors can influence overall health outcomes.
Further studies are needed to tease apart the specific mechanisms through which coastal environments promote longevity, as well as to explore interventions that might help urban populations near inland waters enjoy similar health advantages.
Conclusion
The study from Ohio State University adds important evidence to the growing field of environmental health science, demonstrating a significant association between living near the ocean and increased longevity. The unique benefits of coastal living—milder climates, cleaner air, and enhanced recreational opportunities—appear to offer health advantages that are less accessible to those living near urban inland waters. These insights underscore the value of integrating natural spaces into urban planning and public health strategies, further reaffirming the profound impact of our environment on health and lifespan.
Source: sciencedirect



Comments