5 Minutes
A Paradigm Shift: Is the Universe's Expansion About to Reverse?
For centuries, astronomers and cosmologists have debated the ultimate fate of the Universe—will it expand forever, or is a dramatic end looming in the distant future? Recent research led by scientists from Cornell University and Shanghai Jiao Tong University, among other institutions, challenges long-standing beliefs, offering an intriguing new vision for the cosmos. According to their model, the Universe may stop expanding and start contracting in about 7 billion years, leading to a final "Big Crunch" scenario.
The Science Behind Universal Expansion and Contraction
Understanding Dark Energy and the Role of New Observations
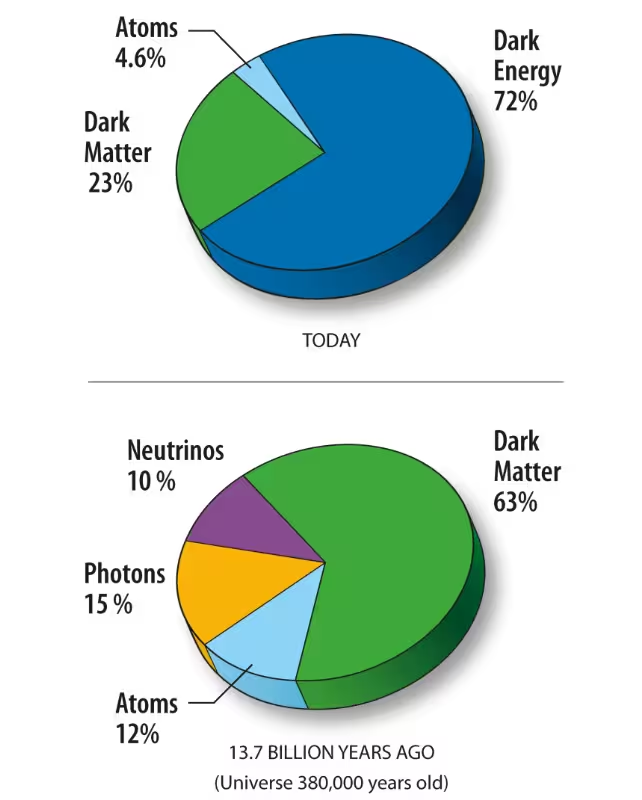
The expansion of the Universe has been driven by a mysterious phenomenon known as dark energy, which constitutes roughly 70% of the cosmos. Traditionally, dark energy was thought to act as a cosmological constant—a steady, unchanging force causing perpetual acceleration of universal expansion. This idea supported the widely accepted theory that the Universe would continue expanding infinitely, growing colder and emptier over time.
However, the new study synthesizes data from leading astronomical surveys, such as the Dark Energy Survey and the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument. Researchers analyzed this data to build a refined cosmic model, challenging prior assumptions. Their results suggest that dark energy may not be truly constant. Instead, its properties could fluctuate over time, fundamentally altering the predicted life cycle of the Universe.

The Axion Model and the Negative Cosmological Constant
Central to this new theory is the incorporation of ultra-light particles known as axions, along with a negative cosmological constant—a term representing a force that would counteract expansion and eventually trigger contraction. Dr. Peter Millington, a theoretical physicist involved in similar work, explains, “Think of the Universe like a giant rubber band. Expansion stretches it out, but negative pressure from dark energy behaves like elasticity, eventually snapping everything back together.”
According to the researchers’ calculations, the Universe is currently about 13.8 billion years old. Their model predicts that outward expansion will gradually slow, reaching its maximum size—approximately 69% larger than today—in roughly 7 billion years. After this peak, the cosmos would transition into a contraction phase, ultimately culminating in a “Big Crunch” about 33.3 billion years from now.
Uncertainties, Alternative Futures, and the Road Ahead
While the findings are groundbreaking, scientists emphasize that these forecasts are highly speculative due to major uncertainties. The concept of a negative cosmological constant remains theoretical with limited observational support. The margin of error in current models is significant, and alternative possibilities—including endless expansion—cannot be definitively ruled out at this point.
Nonetheless, the coming years will be transformative for cosmology. As several major observational projects are set to launch, including next-generation space telescopes and ground-based surveys, astronomers will obtain unprecedented data on dark energy’s true nature. This may soon allow researchers to test, refine, or even disprove the “Big Crunch” hypothesis, bringing us closer to a concrete answer about the Universe’s destiny.
Perspective: Cosmic Timelines and Human Significance
It’s important to remember the vast timescales involved. Even if this model proves accurate, humanity has no reason for immediate concern—20 billion years separate us from the predicted beginning of contraction. To put that in context, complex life on Earth has existed for just 600 million years, and both the death of the Sun and the anticipated collision between the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies will occur long before the Universe starts to shrink.
Conclusion
This study marks a significant milestone in cosmology by offering a specific, testable timeline for the Universe’s ultimate fate. Whether or not the contraction and a "Big Crunch" scenario become reality, this research highlights the rapidly evolving understanding of dark energy and cosmic evolution. As observational technology advances, humanity is poised to answer some of the deepest questions about the nature—and possible endpoint—of everything in existence.



Comments