4 Minutes
Samsung’s 2nm Exynos 2600 Surprises in Early Benchmarks
Samsung’s newly announced Exynos 2600 — the company’s first chipset built on a 2nm GAA (Gate-All-Around) process — is showing promising performance in a recent Geekbench 6 leak. The results suggest Samsung may finally have a flagship-class mobile SoC that can challenge Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Elite Gen 5, at least when the Snapdragon is running in an underclocked configuration.
Benchmark Highlights and CPU Configuration
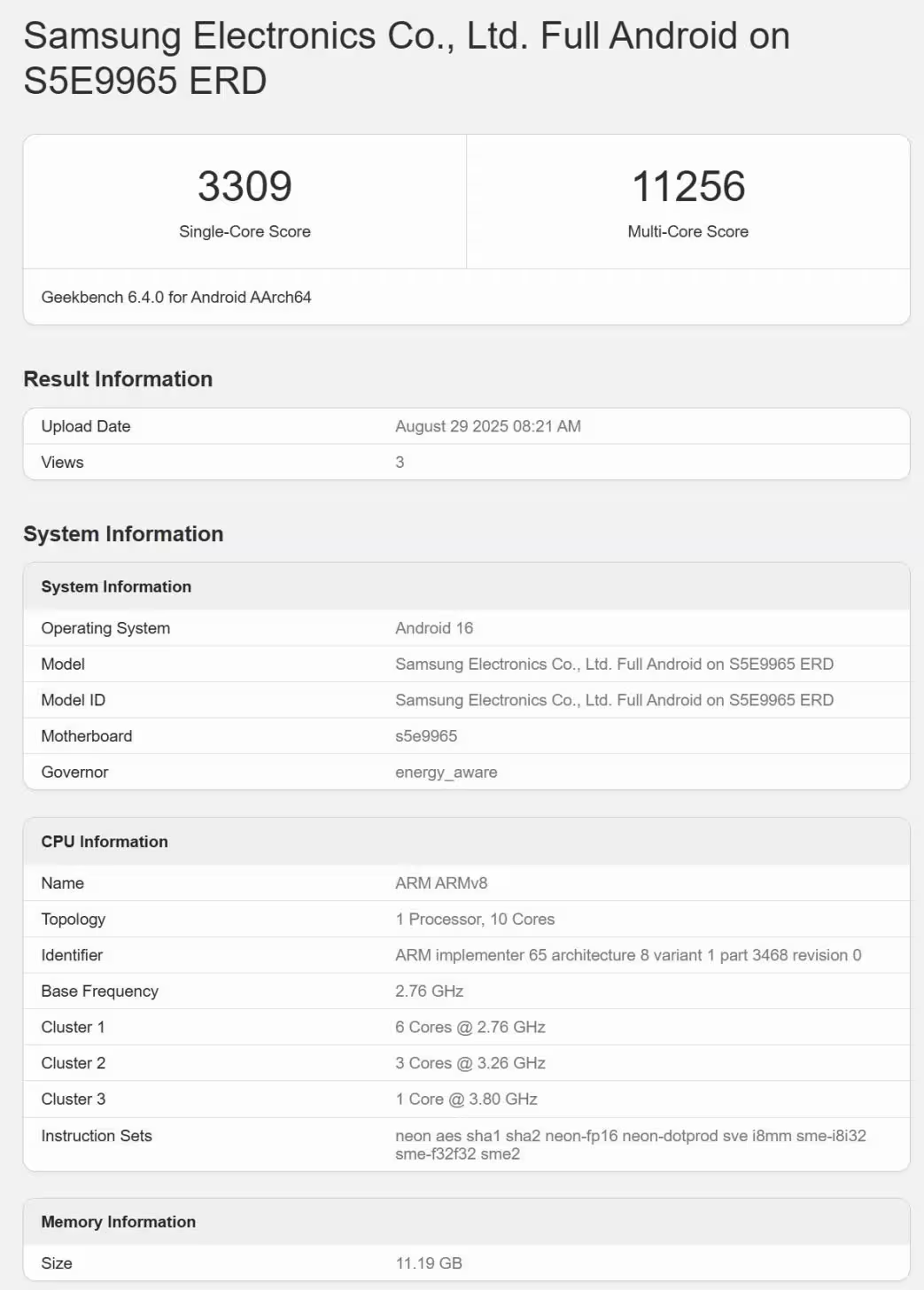
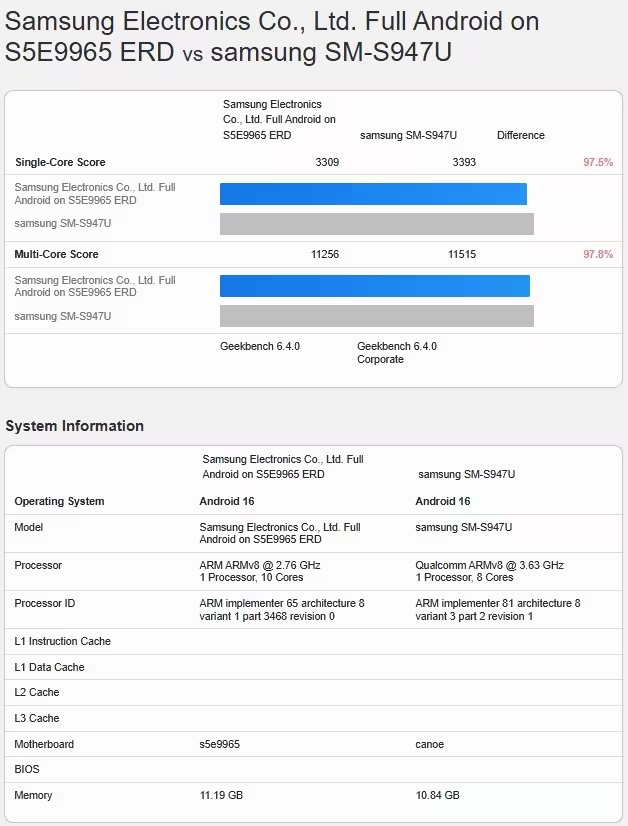
The leaked Geekbench 6 scores list the Exynos 2600 at 3,309 (single-core) and 11,256 (multi-core). For comparison, a Galaxy S26 Edge with a Snapdragon 8 Elite Gen 5 logged 3,393 and 11,515 on the same test — a gap of roughly 2.5 percent. The leak also reveals a 10-core CPU cluster for the Exynos 2600, with the highest-performance core operating at around 3.80GHz. Notably, the Snapdragon result appears to come from a device running its performance cores at 4.00GHz instead of the chip’s peak 4.74GHz, meaning the Qualcomm silicon in that test was effectively underclocked.
What the Numbers Mean
Those Geekbench scores place the Exynos 2600 well ahead of older competitors like the Dimensity 9500 and — more importantly — bring Samsung much closer to Qualcomm’s top-tier performance. Given the Snapdragon test wasn’t at full clock speed, there’s reason to believe the margin could widen either way depending on tuning and thermal management in retail devices.
Features and Architectural Advantages
The Exynos 2600 benefits from Samsung’s 2nm GAA process, which targets better transistor density and power efficiency. The company has also emphasized a significantly improved Neural Processing Unit (NPU) for on-device AI workloads. These upgrades are designed to deliver gains in sustained performance, machine learning inference, camera processing, and energy efficiency — all critical for flagship smartphones like the upcoming Galaxy S26 series.
Comparisons, Advantages and Use Cases
Compared to previous Exynos generations, the 2600 shows a large leap: the leak cites a roughly 53.5% improvement against earlier Exynos results in combined single- and multi-core metrics. Advantages include:
- Stronger single-thread and multi-thread CPU performance suitable for gaming and demanding apps.
- Improved on-device AI performance via a beefed-up NPU for image processing, voice assistants, and AR/ML tasks.
- Potential power-efficiency gains from 2nm GAA that can translate to longer battery life under real-world loads.
Practical use cases where these improvements matter include high-frame-rate mobile gaming, real-time video processing, enhanced computational photography, and local AI inference without cloud latency.
Market Relevance and What Comes Next
If validated in retail devices, the Exynos 2600 could shift Samsung’s competitive position versus Qualcomm and MediaTek. Performance parity or near-parity with the Snapdragon 8 Elite Gen 5—especially when paired with better power management—would strengthen Samsung’s ability to use its own silicon across more Galaxy models and reduce reliance on rivals. However, final verdicts should wait for additional benchmarks that include thermal throttling, sustained workloads, and full-power Snapdragon comparisons.
Bottom Line
The Exynos 2600’s early leak is a promising sign that Samsung’s 2nm GAA strategy is paying off. While the chipset nearly matches an underclocked Snapdragon 8 Elite Gen 5 in Geekbench 6, real-world performance, battery life, and thermal behavior in shipping Galaxy S26 phones will determine whether the Exynos 2600 is truly back in flagship contention.
Source: wccftech


Leave a Comment