6 Minutes
ARM today introduced Lumex, a production-ready compute subsystem (CSS) targeted at 3nm process nodes and designed to speed up how silicon partners build high-performance, power-efficient mobile SoCs. Rather than turning ARM into a chip vendor, Lumex provides turnkey, foundry-ready implementations that manufacturers can use as flexible building blocks — enabling partners to focus their engineering resources on cluster-level differentiation for CPUs and GPUs.
What is Lumex CSS?
Lumex is a modular chipset blueprint for modern smartphones, wearables and other edge devices. It bundles ARM’s next-generation CPU cores, the Mali-G1 GPU family, a scalable system interconnect and security-conscious memory subsystems, all optimized for multiple 3nm foundries. The goal is to shorten development cycles, ensure consistent performance across fabs and make advanced features like secure virtualization and high-efficiency system cache broadly available to OEMs.
Key hardware building blocks
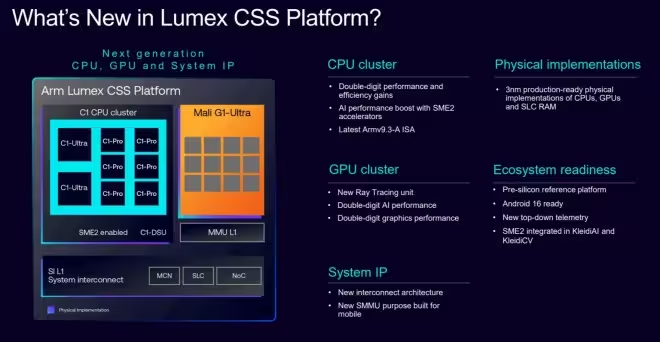
- Scalable CPU clusters via the new C1-DSU (Design System Unit): supports designs from 1 to 14 CPU cores and up to three core types picked from four C1 options.
- Mali-G1 GPU family: scales from 1 to 24 shader cores, including a high-end Mali-G1 Ultra variant.
- System Interconnect L1 & SLC: a system-level cache implementation that reduces leakage by about 71% versus standard RAM approaches, cutting idle power draw.
- MMU L1: a memory management unit tuned for secure and cost-effective virtualization, enabling multi-OS and partitioned workloads on a single SoC.
CPU lineup and performance tiers
ARM's C1-series cores are positioned to cover everything from flagship peak performance to ultra-low-power wearables. The lineup and typical use cases include:
- C1-Ultra — Flagship single-thread performance with roughly +25% single-thread gains and double-digit IPC improvements year-over-year. Ideal for large-model inference, computational photography, content creation and generative AI workloads.
- C1-Premium — Similar peak performance to C1-Ultra but with improved area efficiency (about 35% smaller die area). Suited for upper mid-range devices, multitasking and always-on voice assistants.
- C1-Pro — Tuned for sustained efficiency with +16% sustained performance; aimed at extended video playback, streaming inference and sustained background workloads.
- C1-Nano — Ultra-low-power, compact core delivering up to +26% efficiency in the smallest form factors such as wearables and tiny IoT devices.
GPU, AI and matrix acceleration
The Mali-G1 GPU family scales broadly to fit different market segments. ARM claims the Mali-G1 Ultra achieves roughly 20% better rasterization performance and up to 2x faster ray tracing compared with the previous Immortalis-G925. On inference workloads, the G1 GPU is reported to be about 20% faster versus the prior generation.

At the center of ARM’s AI push is Scalable Matrix Extension 2 (SME2). SME2 accelerates matrix math critical for modern neural networks; ARM reports CPU-side ML workloads can see up to 5x higher throughput and as much as 3x better efficiency compared with earlier designs, making more capable models feasible directly on devices.
Platform-level efficiency and security
Lumex emphasizes power-efficient subsystem design. The System Interconnect L1 and its system-level cache (SLC) cut leakage substantially, reducing idle power — an important win for battery life. The MMU L1 provides hardware-level primitives for secure virtualization, enabling vendors to partition hardware for multiple OSes or isolate sensitive workloads with lower overhead than software-only approaches.

Benchmarks, comparisons and claims
ARM reports a C1 CPU compute cluster tops its previous cores by an average of 30% across six industry benchmarks. Real-world gains vary by workload: gaming and streaming show around a 15% uplift, while everyday tasks like video playback, browsing and social apps improve efficiency by roughly 12% on average. Compared to the Cortex-X925, the C1-Ultra offers double-digit IPC improvements, reinforcing ARM's trajectory toward stronger single-thread and AI performance.
Use cases and market relevance
Lumex is built for a broad spectrum of devices: flagship phones that need maximal performance and advanced on-device AI; upper mid-range handsets that benefit from area-efficient premium cores; sustained power-sensitive tablets and streaming devices; and tiny wearables that demand extreme efficiency. For OEMs and silicon partners, Lumex promises faster time-to-market, consistent cross-foundry implementations at 3nm, and a clear path to integrate heavier on-device AI while retaining battery life and thermal headroom.
Industry response
Several ARM partners welcomed Lumex as a strategic accelerant. Leading OEMs and silicon teams highlighted that a ready-made, customizable compute subsystem removes much of the low-level integration burden and allows them to concentrate on product-level differentiation — whether that’s camera processing, AI features, or system-level power tuning. Major platform vendors also noted SME2 will help bring advanced models to a wider swath of devices, lowering latency and improving privacy by enabling local inference.
Conclusion
Lumex represents a notable shift in how ARM is packaging its IP for the 3nm era: not by becoming a chipmaker, but by delivering a comprehensive, customizable, and production-ready substrate that speeds design cycles and standardizes high-end features like secure virtualization and matrix acceleration. For device makers focused on on-device AI, graphics, and battery-conscious performance, Lumex aims to be a pragmatic shortcut to next-generation mobile compute.
Source: gsmarena


Leave a Comment